Table of Content
FAQ’s on Import License process in India

1. Who is an Authorized officer?
Authorized Officer means a person appointed by the Chief Executive Officer of the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) for the purpose of performing functions (Food Import Clearance) under section 25 of the Act. The powers and duties and responsibilities of Authorized Officer are defined in Chapter IX of Food Safety and Standards (Food Import) Regulations, 2017.
2.What are the pre-requisites for Importing Food into India?
The requirements for importing food into India are as follows:
Mandatory documents:
- The Import- Export Code from DGFT and Import License provided by FSSAI
- The Country of Origin Certificate of the imported product
Mandatory documents that are required according to applicability:
- The Complete Certificate of Analysis including safety parameters from the Country of Origin. This is mandatory for Proprietary Food.
- High Sea Sales Agreement
- Bill of Lading that is mentioned in the Bill of Entry (BoE) for sea consignment
- Ingredients List of the final product
- Specimen of the copy of label
- Declaration that BoE has not been referred on SW (Declaration is required to be in company letterhead.)
- Examination Order
- The list of Transit countries if Food Articles have been transhipped
- Invoice or Proforma Invoice
- Packing List
Self-declaration documents by the importer that are required according to applicability:
- An agreement from importers for the issue of provisional NOC for imported food consignment with less than seven days shelf life.
- An agreement from importers for the issue of provisional NOC for frozen & chilled imported food consignment.
- An agreement from importers for imported food consignment required for Display Purpose in Trade Fair or Exhibition.
- An agreement from importers for imported food consignment required for Personal Use.
- An agreement from importers for imported food consignment required for Research & Development purposes.
- An agreement from importers for imported food consignment required for Sports Events.
- An agreement from importers for imported food consignment containing bulk packages but not having representative samples
- An agreement from importers for imported food consignment containing bulk packages and having representative samples
- An agreement from importers for imported food consignment meant for 100% Export and Re-export.
3.How can importer import food article?
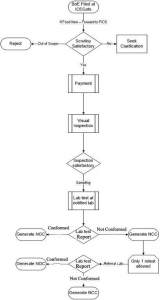
- Bill of Entry (BOE) is filed at the Customs ICE GATE (https://icegate.gov.in) on Single Window Interface for Facilitating Trade (SWIFT). SWIFT is working on Risk-based sampling system which is called as Risk Management System (RMS).
- Risk Management System (RMS) checks the application. If sampling is required; the BOE is referred to FSSAI on online Food Import Clearance System (FICS).
- The CHA or Importer must be registered on FICS (www.ics.fssai.gov.in).
- If necessary FSSAI accepts the BOE and may ask for further details from CHA or Importer.
- Authorized Officer (A.O) fixes an appointment for the inspection of the consignment (only two opportunities are provided to the CHA or Importer to confirm the appointment) if all the relevant information is provided to the authority.
- If everything is found satisfactory on inspection of the consignment including labeling and packaging requirements, the two samples are drawn and if not, Authorised Officer rejects the consignment and issues Non-Conforming Report.
- The samples are then sent to FSSAI Notified Food Laboratory, if sample is found compliant then No Objection Certificate (NOC) is generated and if non-compliant, then Non-Conforming Report (NCR) is generated, rejecting the clearance of food consignment.
- If Importer is not satisfied with the finding of the laboratory report, he may apply for retesting at the referral laboratory. The outcome of test result will determine the future of consignment. The importer may present the review application to the Review Officer (Director, Imports) along with the required documents at the FSSAI Headquarter.
- The order given by the Review Officer can be challenged before the CEO, FSSAI whose decision will be final.
- For more information, please go through FSS Act 2006 and regulations available on the website i.e. www.fssai.gov.in.
- What is the validity period of the Import license in India?
A license granted under Regulation 2.1.7 (1) of FSS (Licensing and Registration of Food Businesses) Regulations 2011 shall be valid for a period of 1 to 5 years. It must be compliant with all conditions of license.
- Do importers required to file an annual return?
Yes, the Food Importer need to file Annual returns according to FSS (Licensing and Registration of Food Businesses) Regulation, 2011.
- Where can I get the list of banned/ restricted products in India?
The list of banned/ restricted products in India is provided by DGFT and can be obtained from their website www.dgft.in.
However, the apex food regulatory may prohibit/restrict the import of any article of Food depending on risk perception or outbreaks of disease, etc. The Food Authority may issue guidelines from time to time for ensuring the safety and wholesomeness of Food imported into India. All such prohibitions and restrictions need to be informed to the Customs immediately.
- What are the specific requirements for labeling Imported Food Items?
Labeling requirements of Imported Food Items are specified under Food Safety and Standards (Packaging and Labelling) Regulations, 2011, Food Safety and Standards (Food Import) Regulations, 2017 and guidelines (only labelling requirement section) dated 23.03.2012 and 09.08.2016 issued by FSSAI.
- What are the rectifiable labelling deficiencies?
The following special dispensation on labeling on imported packaged food consignments are allowed for the rectification at the custom bound warehouse by affixing a single non-detachable sticker or by any other non-detachable method near the principal display panel, like :―
- a) Name and the address of the importer
- b) The Food Safety and Standards Authority (fssai) of India’s Logo and license number
- c) Non-Veg or Veg Logo on the imported product
- d) Category or sub-category along with generic name, nature and the composition for proprietary food.
- What is meant by SWIFT?
Single Window Interface for Facilitating Trade (SWIFT) means the provision of single window system given by the Customs to the importer and Custom House Agent to apply for clearance of import of products.
- What is the Risk based random sampling?
The Risk based random sampling means the activity of drawing samples randomly based on the risk criteria identified and the history of compliance of the importer.
- Which languages can we label particulars need to be declared?
English or Hindi in Devnagri script
- What is Shelf life?
Shelf life means the period between the date of manufacture and the “Best Before” or “Date of expiry” whichever is earlier as printed on the label.
- What is Balance Shelf life of the imported product?
Balance shelf-life means the period between the date of import (Import General Manifest) and “Best Before” or “Date of expiry” as per the food product.
- What is the shelf-life requirements of Imported Food?
The shelf life of not less than sixty percent at the time of import as per Food Safety and Standards (Food Import) Regulations, 2017.
- How many samples are collected per product during the inspection for quality and safety?
Two
- What are the various ways for payment of sampling charges for imported food consignment?
Online payment It is accepted by FSSAIs’ Authorised Officers
- What are the charges required to pay to lab for testing imported food sample?
Charges are Rs. 12000/- per sample for foods for infant nutrition, infant milk food products, infant formula, milk cereal based complementary foods, processed cereal-based complementary foods, packaged drinking water and mineral water.
Rs. 5000/- for all other food categories.
- In what instances the samples are not drawn from the consignment and a rejection report is generated during a visual inspection?
The Authorised Officer does a visual inspection of the imported food product to check compliance under Food Safety and Standards (Packaging and Labelling) Regulations, 2011 in case of imported food consignments. If there is a non-compliance, the Authorised Officer issues a rejection report to Customs Authorities explaining the reasons for refusing the drawl of the sample from the imported food consignment.
- What is the information required on label of sample to be sent to laboratory for analysis?
The information required on the sealed sample of imported food of the Label is:
(a) The Code number of the sample
(b) The date and place of collection of the sample
(c) Quantity of sample
(d) Name of the articles of food and category as per Food Safety and Standards (Food Product Standards and Food Additives) Regulations
(e) The name and quantity of preservatives added while drawing the sample
(f) The name and signature of the Food Importer or his Custom House Agent
(g) The name and signature of the sender with the official seal of the authority.
One of the sealed and labeled Food Sample need to be sent to the Notified Laboratory. The second Food Sample shall be stored in appropriate storage conditions for retesting if it is required in the future.
- Whether drawal of one sample out of the bulk cargo of pulses, other cereals and oils are allowed?
Yes, if the cargo is homogeneous in nature and identity with multiple importers and same exporter, sampling or testing may be done once for the entire consignment and made applicable to all importers.
Sampling is undertaken from the consignment with the first Bill of Entry forwarded by SWIFT. However, can ask importers to provide a NOC or NCC Bill. The analysis report of the sample at the first port of discharge shall also remain valid at other ports of discharge provided the Authorised Officer of FSSAI reseals the remaining cargo at the first port of discharge. The Authorised Officer at the next port of discharge would ensure that the sailing time between the ports of discharge is not unreasonable and that the seal is intact before issuing the NOC for the remaining cargo.
- Is modification of the end-use declaration after applying for clearance allowed for Importer?
No
- What are the conditions where FSSAI NOC is exempted for imported food?
Following are the conditions where FSSAI NOC is exempted for imported food by submitting an undertaking:
- Articles of food imported for personal consumption
- Imported food consignment meant for Display Purpose in Trade Fair or Exhibition
- Imported food consignment meant for Research & Development purposes
- Imported food consignment meant for Sports Events
- Imported food consignment meant 100% Export and Re-export
- What are the conditions where provisional NOCs can be granted to an imported food consignment?
The imported food items having a shelf life of less than 7 days and the food which require special storage conditions can be issued Provisional NOC. In such special cases, without waiting for the analysis report from a laboratory on the basis of an undertaking from the Importer as given by FSSAI.
- Is cleaning and sorting at Customs Bonded warehouse is allowed to improve the quality of food grains including pulse consignments?
Yes, an opportunity can be granted on the request of the importer to improve the quality of the imported food grains by removing foreign matter, mineral matter and damaged grains. The cleaning or sorting of the food grains will be done by the importer strictly under the supervision of the Customs in customs bonded area to make the consignment in accordance to the standards prescribed under FSS (Food Product Standards and Food Additives) Regulation, 2011. NOC will be given by the Authorized Officer, FSSAI, if the sample of the improved product is found to be conforming to the standards.
- Can an Importer get a refund of the fee paid for sampling if samples of the food products are not drawn?
Yes
- Which are the laboratories where imported food samples are sent by FSSAI for analysis?
FSSAI’s notified NABL accredited laboratories
- Whether Importer can apply for a retest if the sample is found Non-compliant to the FSS Standards by the primary laboratory?
Yes
- In which laboratories samples are sent for retest by FSSAI?
FSSAI has notified some Referral laboratories.
- Whether Importer can collect the duplicate samples after obtaining NOC?
Yes
- Do importer gets the copies of Tests reports of all the samples whether granting NOC or NCC?
Yes
- Are duty-free shops at airports outside the scope of FSSAI?
Yes
- Whether the import of nutraceuticals/ health supplements is allowed in India?
Import of nutraceuticals or health supplements as per Order ZF.No.15/Nutraceuticals/FSSAI-2003 dated 06.01.2017 is allowed.
- Is there a requirement for Importer or their representatives to visit the FSSAI Office?
No
- Where importer can clarify the doubts pertaining to the procedure of importing food in India?
The importer can contact six offices i.e Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Tuticorin and Cochin and FSSAI Headquarter at Delhi, and can clarify queries related to import of food in India.
- Where can importer clarify technical queries before importing any food consignment in India?
FSSAI has its Authorised Officers at six regional offices. Their complete addresses including emails are given below for clarification of any technical queries:-
- Which food items are considered as the high risk in case of import into India?
Risk Management system (RMS) by Customs in collaboration with FSSAI considered the following food items as the high-risk food in case of import into India:
- Meat and Meat products
- Fish and Fish Products
- Egg and Egg Products
- Milk powders
- Condensed Milk
- Milk Cereal Base Weaning Foods
- Infant Milk Food
- Infant Formulae
- Fats in any form except edible vegetable oil
- Cocoa butter equivalent or Substitutes
References:
- FAQs_Import_31_03_2017.pdf.Available at: https://fssai.gov.in/home/imports/FAQs-on-Imports.html.Accessible on: 15.05.2019.
Enquire Now
To enquire about our services please complete the form below and we will be in tough with you as soon as possible
Food Regulatory Services
- Consumer Product
- Compliance Services
- Licenses